By: Team W13-1 and Team SE-EDU Since: Jun 2016 Licence: MIT
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Quick Start
- 3. Features
- 3.1. Viewing help :
help - 3.2. Adding a patient:
add-p - 3.3. Listing all patients :
list-p - 3.4. Editing a patient :
edit-p - 3.5. Deleting a patient :
delete-p - 3.6. Search patient by name:
search-p-name - 3.7. Search patient by pid:
search-pid - 3.8. Search patient by appointment status:
search-p-status - 3.9. Advanced search patient by any info:
search-p-advanced - 3.10. Selecting a patient :
select-p - 3.11. Appointment Status Display feature
- 3.12. Adding a doctor:
add-d - 3.13. Listing all doctors :
list-d - 3.14. Selecting a doctor :
select-d - 3.15. Editing a doctor :
edit-d - 3.16. Locating doctor by keywords:
list-d - 3.17. Deleting an existing doctor :
delete-d - 3.18. Finding a doctor for appointment :
match-d - 3.19. Adding a medical history:
add-med-hist - 3.20. Listing medical histories:
list-med-hist - 3.21. Editing write up of medical history:
edit-med-hist - 3.22. Sorting medical history by date:
sort-med-hist - 3.23. Searching medical history :
search-med-hist - 3.24. Viewing a certain medical history:
select-med-hist - 3.25. Adding an appointment:
add-appt - 3.26. Listing appointments :
list-appt - 3.27. Changing an appointment status :
mark-appt - 3.28. Adding a prescription:
add-presc - 3.29. Listing prescriptions:
list-presc - 3.30. Editing description of a prescription:
edit-presc - 3.31. Searching prescriptions :
search-presc - 3.32. Viewing prescriptions:
select-presc - 3.33. Sorting precriptions by date:
sort-presc - 3.34. Listing entered commands :
history - 3.35. Clearing all entries :
clear - 3.36. Exiting the program :
exit - 3.37. Saving the data
- 3.38. Encrypting data files
[coming in v2.0]
- 3.1. Viewing help :
- 4. FAQ
- 5. Command Summary
1. Introduction
DocX is a desktop clinic management application designed for receptionists in small clinics. Even today, many receptionists in small clinics are still using pen and paper to track patients' information, which can be prone to human errors and reduced productivity if the number of patients is large. Our clinic management application is designed specifically to make this process much easier for them.
The features we provide include:
-
Record and manage patients coming to the clinic
-
Record and manage doctors in the clinic
-
Record and manage medical histories of patients
-
Make and manage appointments for patients
-
Record and manage medicines in the clinic and prescriptions given by doctors
While it has a GUI, most of the user interactions happen using a CLI (Command Line Interface). More importantly, DocX is optimized for those who prefer to work with a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI). No technical knowledge on programming or terminal commands is needed. If you can type normal words fast, DocX can get your clinic management tasks done faster than traditional GUI apps.
Interested? Jump to the Section 2, “Quick Start” to get started. Enjoy!
2. Quick Start
-
Ensure you have Java version
9or later installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
docX.jarhere. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your docX.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI should appear in a few seconds.
-
Note that for now, docX only supports Command Line Interface (CLI). Clicking on any list is not allowed and will cause unexpected errors.
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it.
e.g. typinghelpand pressing Enter will open the help window. -
Some example commands you can try:
-
add-pn/John Doe p/98765432 a/22 g/M adr/Utown College: adds a patient namedJohn Doeto docX. -
list-med-hist: lists all medical histories -
add-med-histpid/2 did/8 d/2018-12-09 sw/The patient had a cough. I told him to have a good rest: adds a medical history of patient with specified id(pid) and doctor with specified id(did). -
exit: exits the app
-
-
Refer to Section 3, “Features” for details of each command.
3. Features
Command Format
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user e.g. inadd-p n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asadd-p n/John Doe. -
Items in square brackets are optional e.g
n/NAME [t/TAG]can be used asn/John Doe t/friendor asn/John Doe. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times e.g.[s/SPECIALISATION]…can be used ass/acupuncture,s/acupuncture s/generaletc. -
Parameters can be in any order e.g. if the command specifies
n/NAME p/PHONE,p/PHONE n/NAMEis also acceptable.
3.1. Viewing help : help
Format: help
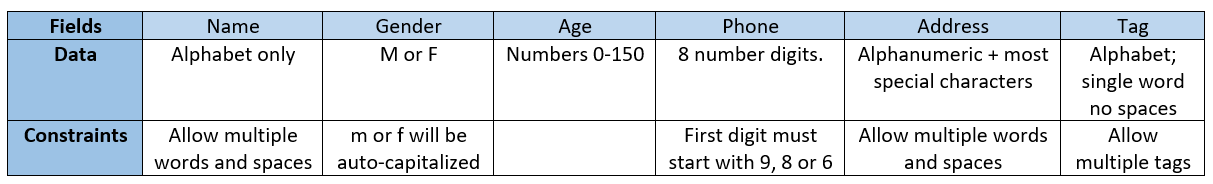
3.2. Adding a patient: add-p
Adds a patient to docX
Format: add-p [n/NAME] [g/GENDER] [a/AGE] [p/PHONE] [adr/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]
Examples:
-
add-p n/Tom Hiddleston g/M a/21 p/98765432 adr/Utown College 2 -
add-p n/Bettany Sim g/F p/82345672 a/32 adr/RVRC House 12 t/diabetic
| For constraints of name, gender, age, phone, address and tags, please refer to the table below. |
-
A new
Patientis thus created with the specified fields with apidand default appointment status ofCOMPLETED.
3.3. Listing all patients : list-p
Shows a list of all patients in docX.
Format: list-p
3.4. Editing a patient : edit-p
Edits an existing patient in docX.
Format: edit-p [INDEX] [n/NAME] [g/GENDER] [a/AGE] [p/PHONE] [adr/ADDRESS]
Examples:
-
edit-p 1 p/91234567
Edits the phone number of the patient with current list index '1' to be91234567. -
edit-p 2 n/Alex Martin p/95678901
Edits the name and phone number of the patient with current list index of '2' to beAlex Martinand '95678901' respectively. -
edit-p 1 n/Alex n/Martin
Having 2 input of the same field will take the last input. Edited patient name toMartin. -
edit-p 1 t/
An empty tag field removes all the current tags of the patient with ID of '1'.
3.5. Deleting a patient : delete-p
Deletes the specified patient from docX.
Format: delete-p [INDEX]
Examples:
-
list-p
delete-p 3
Deletes the patient with current list index of '3' in the docX. -
delete-p 2
Deletes the patient with current list index of '2' in the docX.
3.6. Search patient by name: search-p-name
Search and return patient(s) whose names contain any of the input keywords.
Format: search-p-name [NAME] [NAME2]
Examples:
-
search-p-name Alex
ReturnsAlex LimandAlex Martin -
search-p-name Betsy Tim John
Returns all patients having names containingBetsy,Tim, orJohn
3.7. Search patient by pid: search-pid
Search and return patient(s) whose pid matches the input pid.
Format: search-pid [pid]
Examples:
-
search-pid 1
ReturnsAlex Martinwho has pid of1.
3.8. Search patient by appointment status: search-p-status
Search and return patient(s) whose appointment status matches the input status.
Format: search-p-status [STATUS]
Examples:
-
search-p-status ACTIVE
ReturnsAlex MartinandTom Hiddlestonwho has appointment status ofACTIVE.
3.9. Advanced search patient by any info: search-p-advanced
Search and return patient(s) whose detail contains all of the input keywords,
even if the keyword is only a subword of the patient’s info
Use a "quoted_keyword" to enforce fullword match to the patient’s info
Format: search-p-advanced [keyword] ["quoted_keyword"]…
A patient’s info does not include the list index and "| pid:"
|
Examples:
-
search-p-advanced blood alex
Returns bothAlex Martinwho has abloodclottag andAlexander Flemingwho has ahighbloodpressuretag -
search-p-advanced blood "alex"
ReturnsAlex Martinwho has abloodclottag
and will not returnAlexander Flemingwho has ahighbloodpressuretag -
search-p-advanced "blood" "alex"
Will return neitherAlex Martinwho has abloodclottag
norAlexander Flemingwho has ahighbloodpressuretag
3.10. Selecting a patient : select-p
Select the specified patient from docX.
Displays his/her full information on the browser panel.
Format: select-p [INDEX]
Examples:
-
list-p
select-p 3
Selects the patient with current list index of '3' in the docX
The patient’s full detail can be easily viewed in the browser panel.
3.11. Appointment Status Display feature
The patient card will show the appointment status of a patient. It will display any one of the four enum values: ACTIVE, COMPLETED, CANCELLED, MISSED.
When an appointment is added, or marked, the execution of the command will cascade and alter the status display of the patient.
It follows the following rules:
-
If the patient still has any other active appointments, a patient status will show
ACTIVE -
Else, a patient status will reflect the latest status change to any of his appointment.
3.12. Adding a doctor: add-d
Adds a doctor to docX
Format: add-d n/NAME g/GENDER y/YEAR_OF_EXPERIENCE p/PHONE_NUMBER s/SPECIALISATION
Examples:
-
add-d n/John Doe g/M y/5 p/98765432 s/acupuncture s/general -
add-d n/Betsy Crowe g/f p/81234567 y/22 s/surgery
3.13. Listing all doctors : list-d
Shows a list of all doctors in docX.
Format: list-d
3.14. Selecting a doctor : select-d
Selects an existing doctor in docX to display all the information about this doctor in the browser panel.
Format: select-d INDEX
Examples:
-
select-d 1
Selects the doctor with ID of '1'. -
select-d 5
Selects the doctor with ID of '5'.
3.15. Editing a doctor : edit-d
Edits an existing doctor in docX.
Format: edit-d INDEX [n/NAME] [g/GENDER] [y/YEAR_OF_EXPERIENCE] [p/PHONE] [s/SPECIALISATION]
Examples:
-
edit-d 1 p/91234567
Edits the phone number of the doctor with ID of '1' to be91234567. -
edit-d 2 s/acupuncture s/general
Edits the specialisations of the doctor with ID of '2' to beacupunctureand 'general'.
3.16. Locating doctor by keywords: list-d
Finds doctor(s) whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: list-d [KEYWORD] [KEYWORD]
Examples:
-
list-d John
ReturnsjohnandJohn Doe -
list-d 1
Returns doctor with doctor ID of1, phone number containing1or year of specialisation containing1.
3.17. Deleting an existing doctor : delete-d
Deletes the specified doctor from docX.
Format: delete-d INDEX
Examples:
-
list-d
delete-d 1
Deletes the doctor with ID of '1' in docX. -
delete-d 2
Deletes the doctor with ID of '2' in docX.
3.18. Finding a doctor for appointment : match-d
Lists the doctors whose specialisations match and are free for an appointment at the stated date and time.
Format: match-d s/SPECIALISATION d/DESIRED_DATE_OF_APPT t/DESIRED_START_TIME_OF_APPT
Examples:
-
match-d s/acupuncture d/2019-06-02 t/10:00
Lists the doctors who has the specialisation ofacupunctureand is free on 2nd June 2019 at 10am. -
match-d s/general d/2019-10-04 t/15:00
Lists the doctors who has the specialisation ofgeneraland is free on 4th October 2019 at 3pm.
3.19. Adding a medical history: add-med-hist
Adds a medical history
Format: add-med-hist pid/PATIENT_ID did/DOCTOR_ID d/DATE sw/SHORT_WRITEUP
Examples:
-
add-med-hist pid/1 did/7 d/2019-03-05 sw/Came down with a stomach flu, possibly due to eating expired food -
add-med-hist pid/3 did/8 d/2018-07-09 sw/Had a fever with sore throat. Sleeps late.
3.20. Listing medical histories: list-med-hist
Show a list of all medical histories or medical histories with specified constraint(s).
Format: list-med-hist [pid/PATIENT_ID] [did/DOCTOR_ID] [d/DATE]
Examples:
-
list-med-hist: show all medical histories in docX -
list-med-hist pid/1: show all medical histories of patient with id 1. If patient with id 1 is already deleted or not in docX, an error will be shown. -
list-med-hist pid/1 d/2019-03-03: show all medical histories of patient with id 1 which happened on 2019-03-03
3.21. Editing write up of medical history: edit-med-hist
Edit the write up of medical history with specified index in medical history list.
Format: edit-med-hist INDEX sw/EDITED_WRITEUP
Examples:
-
edit-med-hist 1 sw/The patient came to me this morning, having a fever. This afternoon he came again because of higher fever.
3.22. Sorting medical history by date: sort-med-hist
Sort medical history by date in ascending order or descending order.
Format: sort-med-hist [ASC/DESC]
Examples:
-
sort-med-hist
Medical histories will be listed from newest date to oldest date -
sort-med-hist ASC
Medical histories will be listed from oldest date or newest date.
3.23. Searching medical history : search-med-hist
Finds medical history(ies) whose write up contains any of the given keywords.
Format: search-med-hist KEYWORD
Examples:
-
search-med-hist fever
Returns all medical history with the write up containing the keywordfever -
search-med-hist fever sore
Returns all medical history with the write up containing either 'fever' or 'sore' or both keywords.
3.24. Viewing a certain medical history: select-med-hist
View details specified medical history with index in displayed list.
Format: select-med-hist index
Examples:
-
select-med-hist 1
Returns details of the medical history with index 1 in medical history list.
3.25. Adding an appointment: add-appt
Adds an appointment between a patient and a doctor
Format: add-appt pid/PATIENT_ID did/DOCTOR_ID d/DATE_OF_APPT t/START_TIME
Examples:
-
add-appt pid/1 did/7 d/2019-06-01 t/09:00
Adds an appointment with patient ID '1' and doctor ID '7' on 1st June 2019 at 9am. -
add-appt pid/3 did/9 d/2019-06-01 t/13:00
Adds an appointment with patient ID '3' and doctor ID '9' on 1st June 2019 at 1pm.
3.26. Listing appointments : list-appt
Shows a list of appointments in the system. Can be used with or without optional keywords to filter the result.
Format: list-appt [pid/PATIENT_ID] [did/DOCTOR_ID] [d/DATE_OF_APPT] [t/START_TIME] [s/STATUS] [c/CHRONOLOGY]
Examples:
-
list-appt
Lists all appointments. -
list-appt c/FUTURE
Lists all appointments that are in the future. -
list-appt pid/1
Lists all appointments with patient ID 1. -
list-appt pid/1 did/7
Lists all appointments with patient ID 1 and doctor ID 7. -
list-appt d/2018-06-01 t/09:00
Lists all appointments with date 2018-06-01 and time 09:00. -
list-appt s/ACTIVE
Lists all appointments that are marked as ACTIVE.
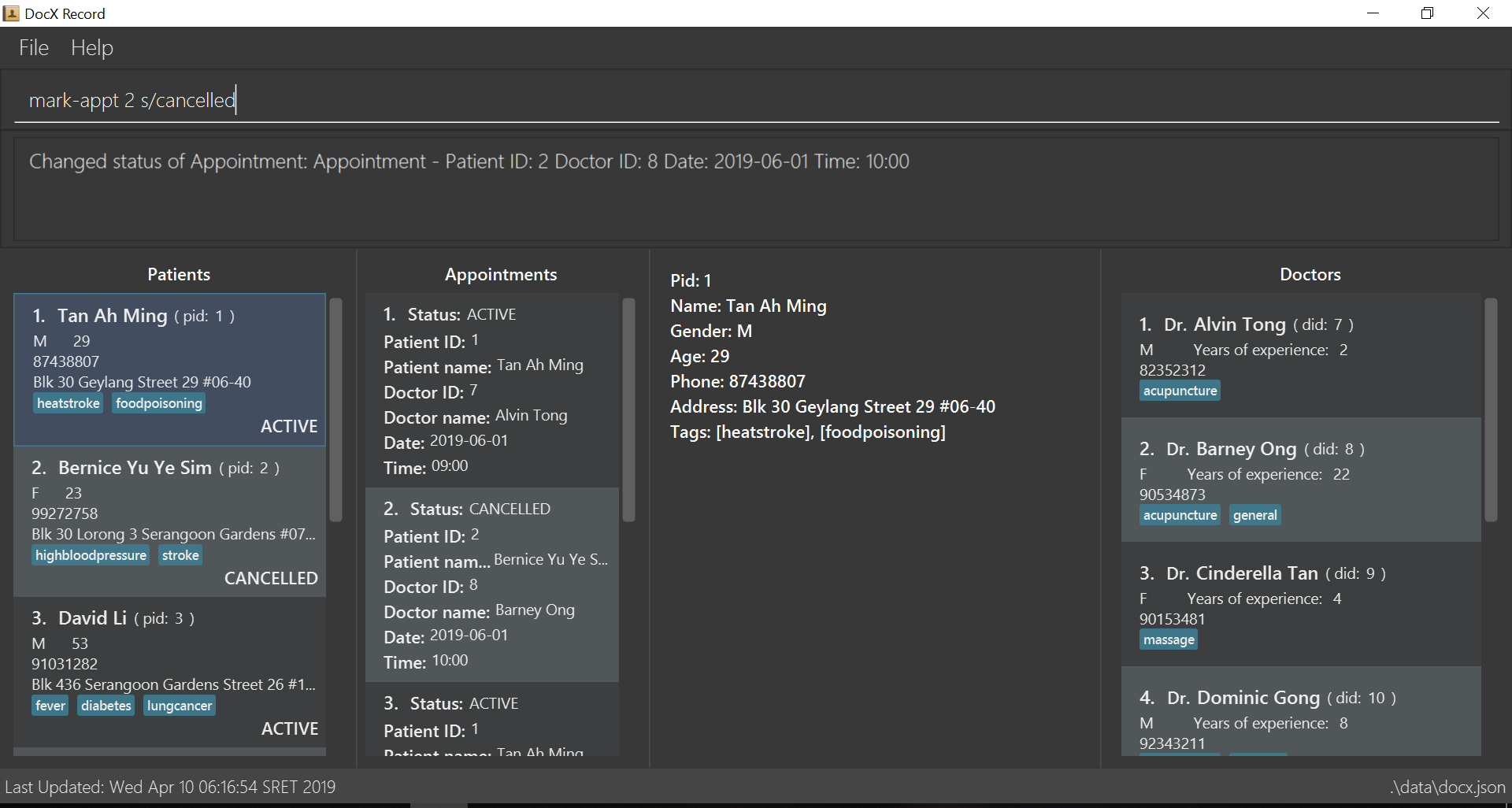
3.27. Changing an appointment status : mark-appt
Mark an appointment as ACTIVE, CANCELLED, MISSED or COMPLETED
Format: mark-appt INDEX s/NEW_STATUS
Examples:
-
mark-appt 1 s/CANCELLED
The appointment with INDEX 1 is cancelled. -
mark-appt 3 s/MISSED
The appointment with INDEX 3 was missed. Note that this can only be done to elapsed appointments.
3.28. Adding a prescription: add-presc
Adds a prescription and the prescribing doctor under the patient involved.
Format: add-presc pid/PATIENT_ID did/DOCTOR_ID dp/DATE rid/MED_ID w/SHORT_WRITEUP
Examples:
-
add-presc pid/1 did/2 dp/2018-05-13 mn/Acetaminophen d/500 mg for relieving pain
Adds the prescribing doctor with ID of '2', the medicine with name of 'Acetaminophen', and a short description of '500 mg for relieving pain' under the patient with ID of '1' on the date May 13rd 2018. -
add-presc pid/5 did/3 dp/2018-05-13 mn/Aspirin d/2g for curing fever
Adds the prescribing doctor with ID of '3', the medicine with name of 'Aspirin', and a short description of '2g for curing fever' under the patient with ID of '5' on the date May 13rd 2018.
3.29. Listing prescriptions: list-presc
Show a list of all prescriptions with the specified requirements.
Format: list-presc [pid/PATIENT_ID] [did/DOCTOR_ID]
Examples:
-
list-presc
Lists all past prescriptions. -
list-presc pid/3
Lists all past prescriptions whose patientId is '3'. -
list-presc pid/3 did/5
Lists all past prescriptions whose patientId is '3' and doctor id is '5'.
3.30. Editing description of a prescription: edit-presc
Edit the description of the prescription with specified index in prescription list.
Format: edit-presc INDEX d/EDITED_DESCRIPTION
Examples:
-
edit-presc 1 d/For curing fever
3.31. Searching prescriptions : search-presc
Finds prescriptions whose description contains any one of the specified keywords.
Format: search-presc KEYWORDS
Examples:
-
search-presc fever
All prescriptions with descriptions containing the keywordfeverwill be listed. -
search-presc fever cold
All prescriptions with descriptions containing the keywordfeverorcoldwill be listed.
3.32. Viewing prescriptions: select-presc
View details of the specified prescription with index in the displayed list.
Format: select-presc INDEX
Examples:
-
select-presc 1
List details of the prescription with index 1 in displayed prescription list.
3.33. Sorting precriptions by date: sort-presc
Sort prescriptions by date in ascending order or descending order.
Format: sort-presc [ASC/DESC]
Examples:
-
sort-presc
Prescriptions will be listed from newest date to oldest date -
sort-presc ASC
Prescriptions will be listed from oldest date or newest date.
3.34. Listing entered commands : history
Lists all the commands that you have entered in reverse chronological order.
Format: history
|
Pressing the ↑ and ↓ arrows will display the previous and next input respectively in the command box. |
3.35. Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all entries from docX.
Format: clear
3.36. Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
3.37. Saving the data
DocX data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data.
There is no need to save manually.
3.38. Encrypting data files [coming in v2.0]
The user will be able to enable/disable the encryption of data files through a button in the menu bar.
4. FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous DocX folder.
5. Command Summary
PATIENT COMMANDS
-
Add a new patient
add-p [n/NAME] [g/GENDER] [a/AGE] [p/PHONE] [adr/ADDRESS] [t/TAG] -
List existing patients :
list-p -
Edit an existing patient :
edit-p [INDEX] [n/NAME] [g/GENDER] [a/AGE] [p/PHONE] [adr/ADDRESS] [t/TAG] -
Delete an existing patient :
delete-p [INDEX] -
Searching a patient by name :
search-p-name [NAME] -
Searching a patient by pid :
search-pid [pid] -
Searching a patient by appt status :
search-p-status [STATUS] -
Searching a patient (advanced) :
search-p-advanced [KEYWORD] ["QUOTED_KEYWORD"]
DOCTOR COMMANDS
-
Add a new doctor
add-d n/NAME g/GENDER y/YEAR_OF_SPECIALISATION p/PHONE_NUMBER s/SPECIALISATION
e.g.add-d n/Aaron Doe g/Male y/3 p/98765432 s/`acupuncture' 'general' -
List all existing doctors :
list-d -
Select a doctor :
select-d INDEX
e.g.select-d 3 -
Edit an existing doctor :
edit-d INDEX [n/NAME] [g/GENDER] [a/AGE] [p/PHONE] [s/SPECIALISATION]
e.g.edit-d 2 n/Betsy Crower p/45678901 -
Locating doctor(s) by keywords :
list-d KEYWORD [KEYWORD]
e.g.list-d john 8233 -
Finding a doctor for an appointment :
match-d s/SPECIALISATION d/DESIRED_DATE_OF_APPT t/DESIRED_TIME_OF_APPT
e.g.match-d s/acupuncture d/2019-06-02 t/09:00 -
Delete an existing doctor :
delete-d INDEX
eg.delete-d 2
MEDICAL HISTORY COMMANDS
-
Add a new medical history :`add-med-hist pid/PATIENT_ID did/DOCTOR_ID d/DATE sw/SHORT_WRITEUP`
e.g.add-med-hist pid/1 did/7 d/2019-03-03 sw/Had a fever with sorethroat. Sleeps late. -
List medical histories :
list-med-hist [pid/PATIENT_ID] [did/DOCTOR_ID] [d/DATE]
e.g.list-med-hist d/2019-03-03 -
Edit write up of an existing medical history :
edit-med-hist INDEX sw/EDITED_WRITEUP
e.g.edit-med-hist 1 sw/The patient came this morning with high fever. In the afternoon, he came with higher fever. -
Sort medical histories by date :
sort-med-hist [ASC/DESC]
e.g.sort-med-hist DESC -
Search a medical history :
search-med-hist KEYWORD
e.g.search-med-hist fever -
Select a medical history :
select-med-hist INDEX `
e.g. `select-med-hist 1
APPOINTMENT COMMANDS
-
Add a new appointment
add-appt pid/PATIENT_ID did/DOCTOR_ID d/DATE_OF_APPT t/START_TIME
e.g.add-appt pid/1 did/1 d/2019-06-01 t/09:00 -
Listing appointments
list-appt [pid/PATIENT_ID] [did/DOCTOR_ID] [d/DATE_OF_APPT] [t/START_TIME] [s/STATUS] [c/CHRONOLOGY]
e.g.list-appt -
Changing an appointment status :
mark-appt INDEX s/NEW_STATUSe.g.mark-appt 1 s/CANCELLED
PRESCRIPTION COMMANDS
-
Add a new prescription
add-presc pid/PATIENT-ID did/DOCTOR-ID dp/DATE mn/MEDICINE NAME d/SHORT DESCRIPTION
e.g.add-presc pid/1 did/2 dp/2018-05-13 mn/Acetaminophen d/500 mg for relieving pain -
List prescriptions :
list-presc [pid/PATIENT-ID ] [did/DOCTOR-ID ]
e.g.list-presc pid/1 did/2 -
Edit description of an existing prescription
edit-presc INDEX (must be a positive integer) d/EDITED-DESCRIPTION
e.g.edit-presc 1 d/For curing fever -
Sort prescriptions by date :
sort-presc [ASC/DESC]
e.g.sort-presc ASC -
Search a prescription :
search-presc KEYWORDS
e.g.search-presc fever -
Select a prescription :
select-presc INDEX
e.g.select-presc 1
GENERAL COMMANDS
-
Help :
help -
History :
history